What ADHD Looks Like at Every Age: From Childhood to Adulthood
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood and often continues into adulthood, affecting millions worldwide. Its hallmark symptoms include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, but the way these symptoms manifest evolves significantly as individuals progress through different life stages. Recognising ADHD symptoms in kids, identifying signs of ADHD in adults, knowing how the diagnosis of ADHD in children is conducted, and understanding effective ADHD symptoms and treatment strategies are essential for better management and improved quality of life. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at ADHD across the lifespan, emphasising how symptoms and treatments are tailored at every age to support individuals living with ADHD.
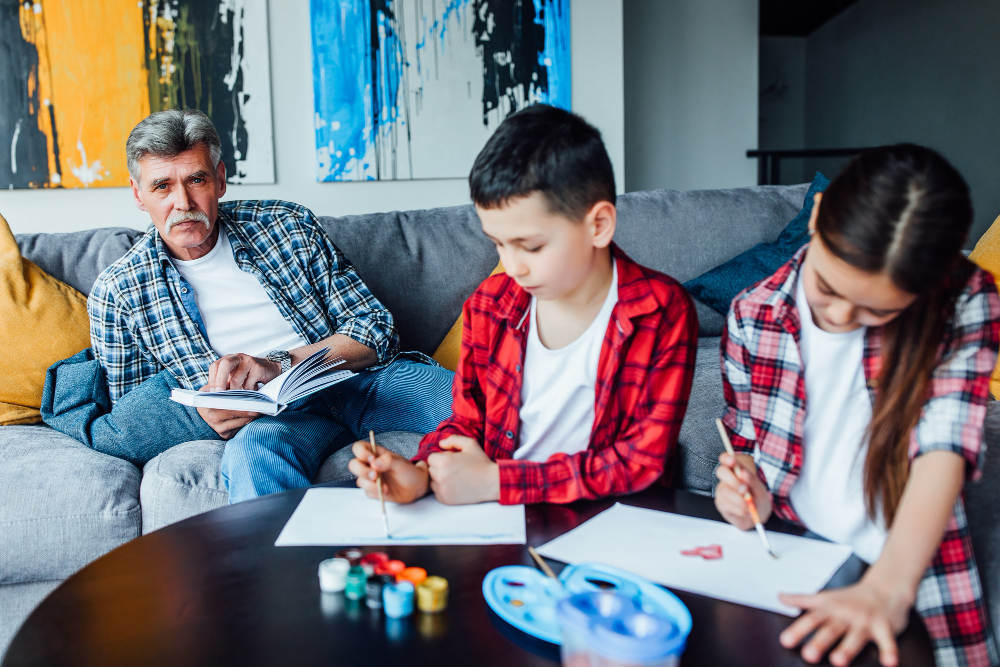
ADHD Symptoms in Kids: Early Indicators and Impact
ADHD symptoms commonly appear as difficulty sustaining attention during tasks or play, frequent careless mistakes, and trouble following instructions. Hyperactivity manifests as constant fidgeting, running or climbing in inappropriate situations, and excessive talking. Impulsivity is evident when kids interrupt conversations, grab things without permission, or have difficulty waiting their turn. These symptoms interfere with learning and social development, often leading to academic struggles and challenges with peer relationships. Recognising these early ADHD symptoms in kids is critical because timely diagnosis allows families and educators to implement supportive interventions. Diagnosis typically involves collecting information from multiple sources, including parents, teachers, and clinicians, to confirm that symptoms are pervasive and impair functioning in settings like home and school.
Diagnosing ADHD in Children: Thorough Assessment for Accurate Identification
ADHD diagnosis is a multi-step process that requires symptoms to have appeared before age 12 and to persist for at least six months with significant impairment. Comprehensive evaluation includes standardised rating scales, clinical interviews, observations, and ruling out other conditions such as anxiety, learning disorders, or mood problems that might mimic ADHD. For diagnosing ADHD in children, symptoms must be evident in at least two settings to ensure behaviours are not context-specific. Early and precise diagnosis is fundamental to creating an effective treatment plan that often integrates behavioural therapy for ADHD, educational accommodations, and sometimes medication.
Signs of ADHD in Adults: The Subtle Yet Impactful Presentation
In adults, the symptoms often differ from those in children and may be less obvious yet profoundly affect daily life. Adults with ADHD commonly experience chronic issues with attention, organisation, and time management. Internal restlessness replaces the overt hyperactivity seen in children but still prompts feelings of impatience and difficulty relaxing. Impulsivity can manifest as interrupting others or making hasty decisions that have social or financial consequences. Emotional dysregulation, including mood swings and irritability, is frequent. Diagnosing ADHD in adults can be challenging, requiring a careful review of childhood symptoms alongside current difficulties. Many adults remain undiagnosed until their struggles cause significant disruptions in work or relationships, underscoring the importance of awareness regarding the signs of ADHD in adults.
ADHD Symptoms and Treatment: Managing Across the Lifespan
ADHD has no known cure, but numerous evidence-based treatments exist to manage symptoms and enhance functioning at all ages. The approach to ADHD symptoms & treatment typically blends behavioural therapies, medication, and lifestyle adjustments customised according to age and individual needs:
In preschool children (ages 4-5), behaviour therapy focusing on parent training is the first-line treatment. Techniques involve establishing routines, positive reinforcement, and environmental modifications to reduce distractions and improve self-regulation.
For school-age children, stimulant medications such as methylphenidate and amphetamines are commonly prescribed alongside behavioural interventions and academic supports to improve attention and impulse control and reduce hyperactivity. Nonstimulant medications offer alternatives for those intolerant to stimulants. Classroom strategies might include preferential seating, frequent breaks, and task breakdowns.
Adolescents benefit from continued behavioural therapy for ADHD & support emphasising executive functioning skills like organisation, time management, and emotional regulation, coupled with medication when indicated. Therapy can also address coexisting conditions such as anxiety or depression.
Signs of ADHD in adults often need to be managed with a holistic treatment plan that combines pharmacotherapy with cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and ADHD coaching. CBT helps address negative thought patterns, improve self-discipline, and develop coping strategies for workplace and relationship challenges. Medication options for adults include stimulants, nonstimulants, and antidepressants tailored to individual symptom profiles and tolerance.
Across all ages, lifestyle changes contribute significantly to symptom management. Adequate sleep, regular physical activity, mindfulness practices, and stress management techniques such as meditation or deep breathing support brain health and emotional balance.
Stress Management and Mindfulness: Complementary Approaches
Stress can exacerbate ADHD symptoms, so incorporating stress reduction strategies enhances treatment effectiveness. Mindfulness practices and relaxation training promote emotional regulation and attention control by cultivating awareness and reducing impulsive reactions. Techniques like goal setting, self-monitoring behaviours, and visualisation support self-regulation skills in school and work settings. These approaches, combined with traditional treatments & ADHD coaching, improve overall quality of life and resilience.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Ongoing Support
Understanding ADHD symptoms & treatments is imperative. Starting treatment early improves long-term outcomes by mitigating academic difficulties and social challenges in children. Equally, continued support during adolescence and adulthood fosters independence and adaptation to evolving life demands. ADHD symptoms may diminish in intensity with age but rarely disappear entirely; therefore, a lifelong approach to management that adapts to changing needs is vital.
Conclusion
ADHD is a complex, lifelong condition with symptoms that change across childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Diagnosing ADHD in children, understanding how it manifests in adults, and following a rigorous process of diagnosis are all fundamental to helping individuals manage their condition effectively. Combining behavioural therapies, medications, and lifestyle modifications tailored to each stage can empower those with ADHD to navigate challenges and realise their potential.
Ankita Jagtiani is a certified life, POSH, and ADHD coach dedicated to guiding individuals through their ADHD journey and unlocking their full capabilities.